Skills :
Data Science, Data Analysis, Social Psychology Research, Behavioral Research, Python.Tools :
Google Colab, Python Libraries: Numpy, Pandas, Seaborn, Matlplotlib, Scipy, Sklearn.Links :
ColabBackground
To support pro-environmental efforts by the school board & local government, I researched declining rates of students biking to school.
Target
Understanding Biking Behavior and Analyzing Factors Affecting Intention to Use Bike to School among School Students.
What did this research find out?
- Distance is a key factor in encouraging students, especially girls, to use bikes to get to school. Intention can also play a role, especially for boys.
- Perceived behavioral control is the most important factor influencing the intention to use a bike to travel to school, for both for boys and girls.
- Attitudes towards biking to school are heavily influenced by two main beliefs: the perception that biking makes students healthier and how important, enjoyable, and beneficial this is for them, as well as the view that using bicycles consumes more energy that could otherwise be used for activities like studying, along with how important, concerning, and disadvantageous they find this aspect.
- Subjective norms are greatly influenced by two key beliefs: the extent to which students perceive that their friends would enjoy and approve of biking to school, along with the strength of their desire to meet these expectations, and the extent to which they believe that teachers would also enjoy and expect them to bike to school, coupled with the strength of their desire to comply with these expectations.
- Two dominant beliefs significantly influence the formation of perceived behavioral control. The first is their belief about whether distance is a facilitating or hindering factor, and how easy or difficult it is to use a bike to get to school considering this factor. The second is their belief about the energy required to use bicycles to school, and how easy or difficult it is to use bicycles considering this factor.
Insights & recommendation:
- Government might want to apply programs aimed at encouraging prospective students to choose schools closer to their homes as the research shows that distance plays an important role in influencing students to use bike to get to school.
- More programs implemented by schools, the local government, or other public institutions should focus on persuasive information emphasizing the personal benefits of biking (eg. health impacts) rather than on the more moral or social information (eg. environmental impacts).
- More programs conducted by schools, the local government, or other public institutions that aim to instill the belief among students that biking to school is socially accepted and favored among teenagers. This can be achieved by considering current teenage culture and leveraging conformity among teenagers and peer relationships.
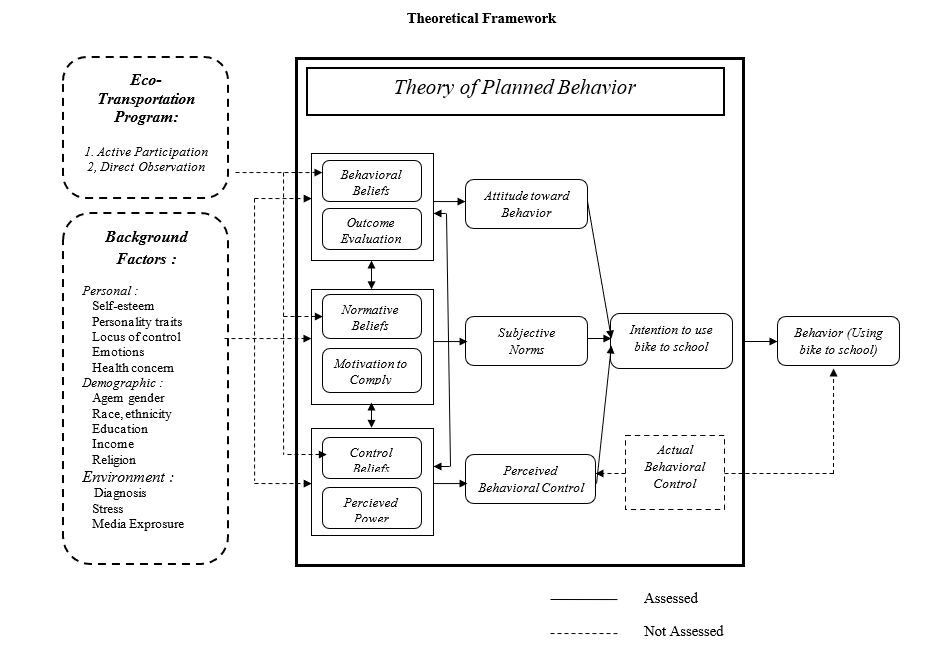 Figure 1: Theory of Planned Behavior
Figure 1: Theory of Planned Behavior
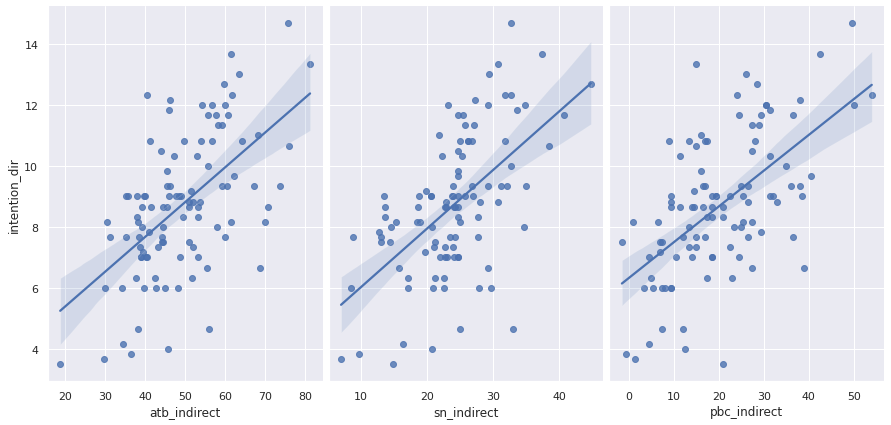 Figure 2: Regression Model
Figure 2: Regression Model
 Figure 1: Features Histogram
Figure 1: Features Histogram
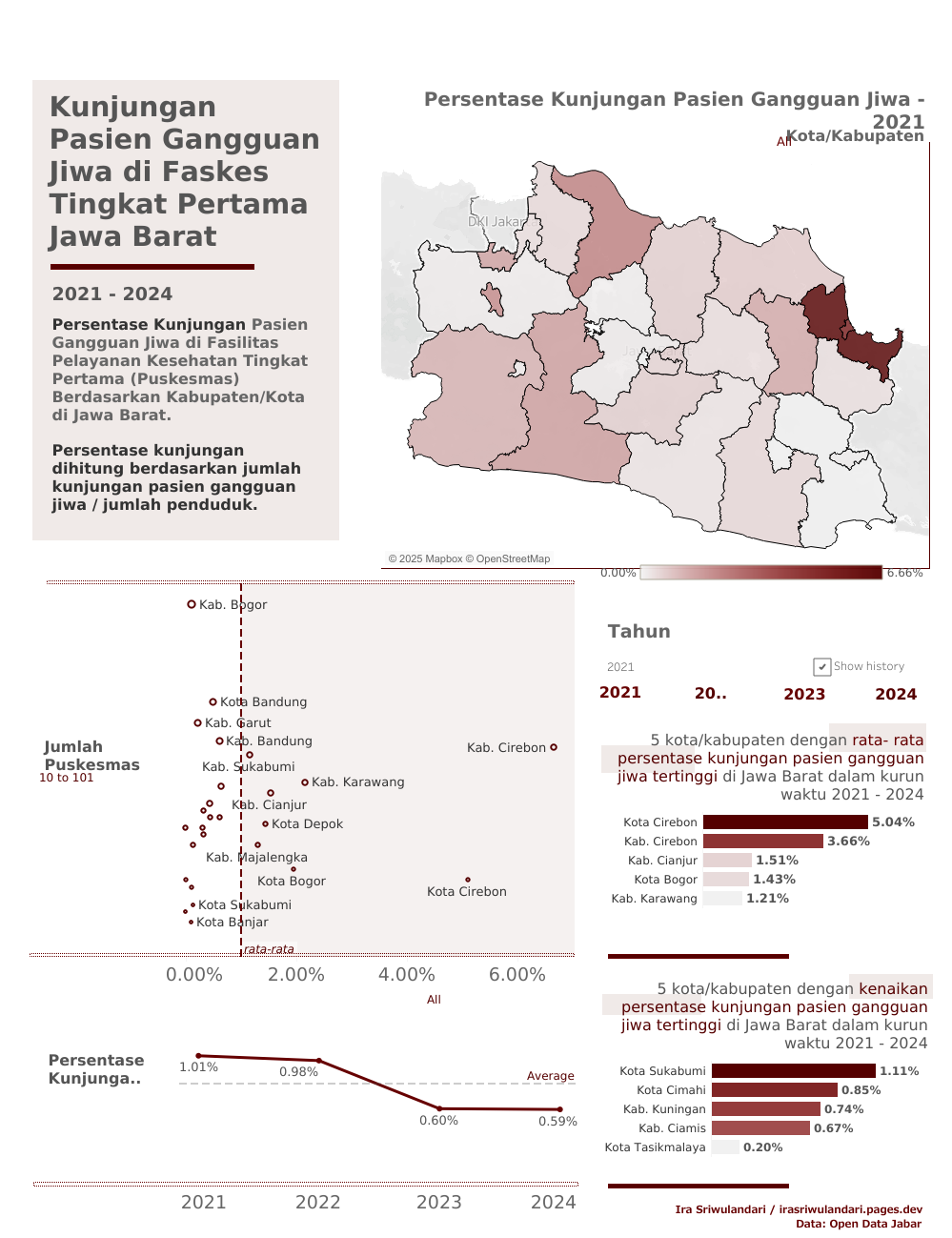 Figure 1: Tableau
Figure 1: Tableau
 Figure 2: Looker
Figure 2: Looker